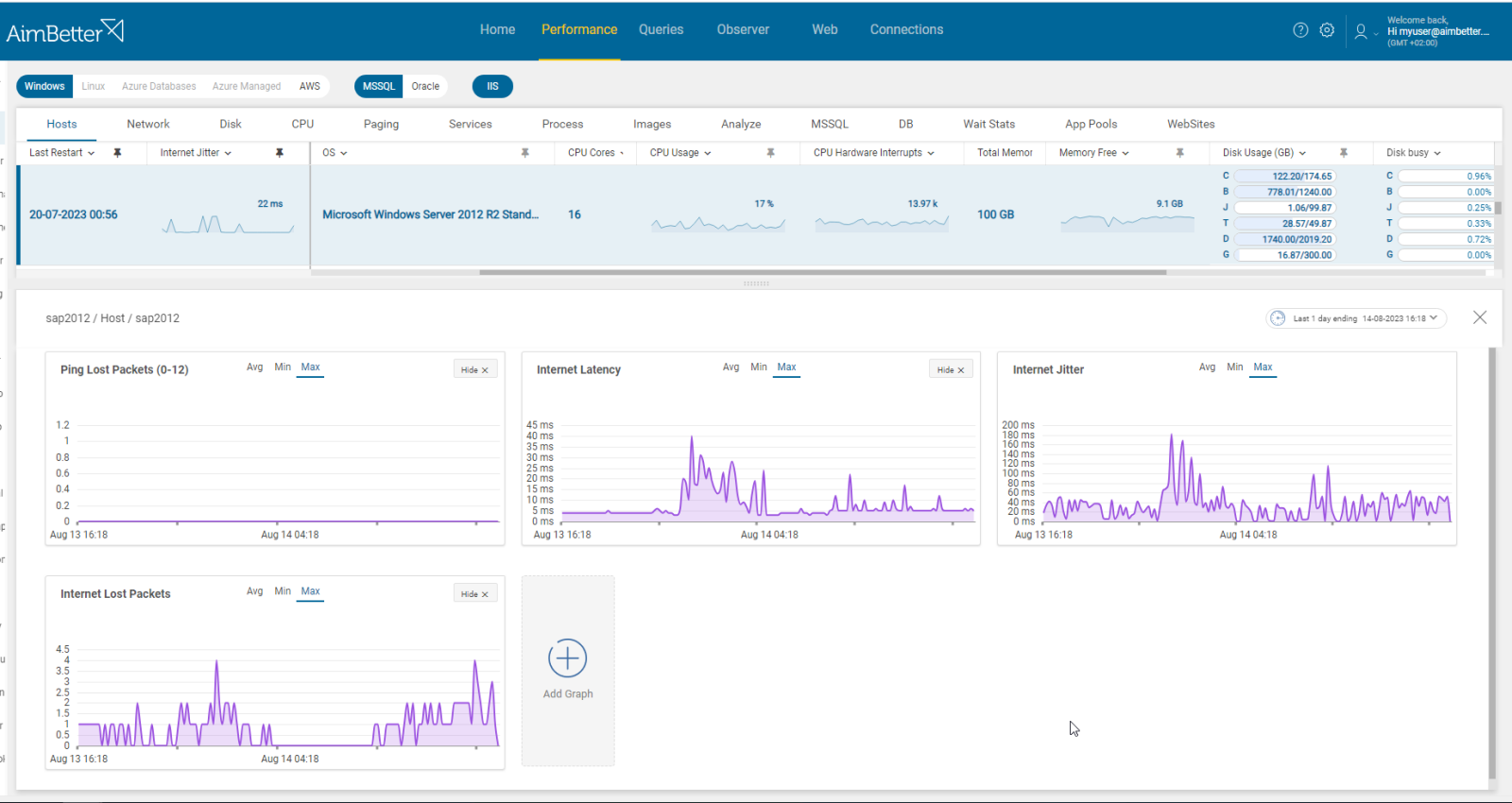
The occurrence of lost packet alerts indicates a disruption in communication with the internet, resulting in either no response or partial response, potentially leading to user experience delays and process hang-ups. In situations where the internet is unresponsive, all traffic between users and external resources halts, while missing packets can affect application functionality and performance. Packet retries, in particular, can significantly increase network traffic load, and delays in queries waiting for data can elevate the risk of blocks, deadlocks, and increased page file activity due to locked buffer pool space.
AimBetter monitors the success of ping commands sent to the internet target (google.com) every 5 seconds, assessing network connection health based on response success and latency.
Find out how you can save hours of work when investigating the root cause of this issue.
Symptoms
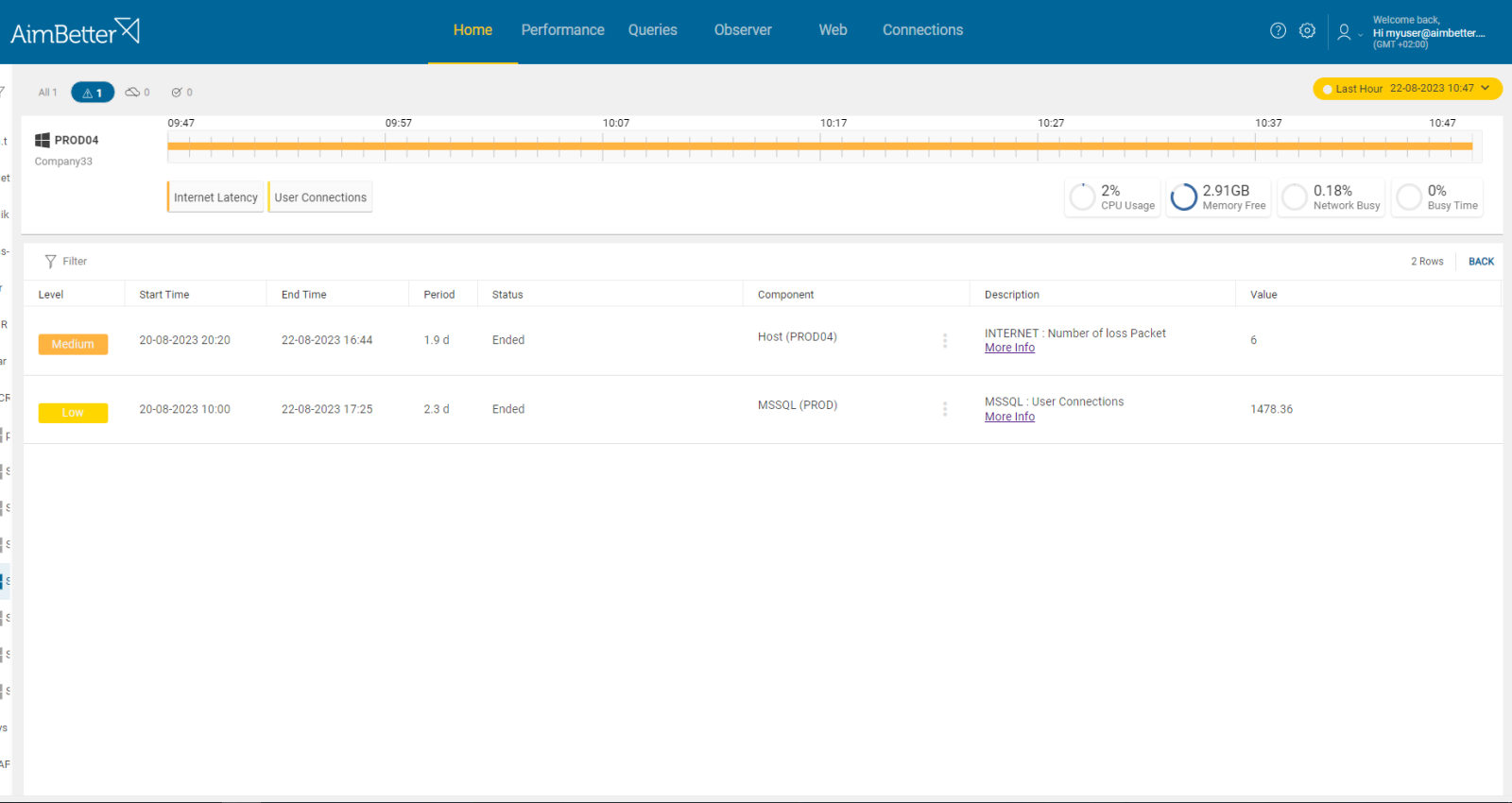
The server is either unresponsive or experiencing packet loss, resulting in communication issues with the SQL server, leading to either no response or only partial responses.
Impact: Medium
In addition to user-experienced delays, there’s a risk of data loss. If the server becomes unresponsive, all communication between the user and the server will cease. Furthermore, missing packets can impact application functionality and performance, potentially leading to increased instances of blocks, deadlocks, and elevated page file activity due to locked buffer pool space
Expected behavior
The server is expected to respond to every ping command. If there are 12 consecutive ping failures, it indicates a severe issue that requires immediate attention.
Possible causes
1- Network load. Priority: Medium
When network traffic surpasses the capacity of the infrastructure, leading to high network load, processing and forwarding of data packets can be delayed, potentially resulting in packet loss. These delays in network traffic can consequently slow down data transmission, increasing internet latencies and further exacerbating the risk of packet loss.
Problem identification:
Check current traffic and which applications use most of it. Compare it with historical patterns of network traffic or during times of lower network traffic.
- Using a network monitoring tool, you can analyze the volume of traffic passing through your network and identify the applications or devices consuming the most bandwidth. While many monitoring tools excel at identifying when issues begin, they often lack direct comparison features across different time frames.
- Measure traffic during times of lower network demand, for that you should wait for this time since you don’t have historical data about performance.
- Compare the results with the current packet loss rates (which causes internet packet loss).
- Review your network logs to see if there are any unusual patterns. This might be a time-consuming task, yet crucial for identifying potential issues or anomalies.
Recommended action :
Check network traffic loads with a network analyzer, including tracking with ping tests or a monitoring tool for internet packet loss. Move high-volume traffic like remote storage and backups onto a secondary network if possible.
2- Incorrect network settings. Priority: Medium
Read our network utilization article regarding inefficient network structure.
Recommended action :
Optimize the settings (DNS, IP change, or card bandwidth) to improve network capacity. If necessary, upgrade to faster components wherever bottlenecks are occurring.
3-Large data transfer in the network. Priority: Medium
When data is transmitted across a network, it is broken down into packets that are transmitted individually and then reassembled at the destination. If the volume of data transfer is too large, it can potentially result in packet loss.
Problem identification:
Actively follow the data transmission volume in parallel to packet loss.
- Using a network monitoring tool, check how much traffic flows through your network. Depending on the monitoring tool, you may get a notification when the problem starts, but can’t compare time frames.
- Run ping tests to measure latency and packet loss before, during, and after large data transfers. Look for patterns of increased packet loss during times of large data transfers.
- Measure the amount of bandwidth being used during the data transfer. Large values may indicate packet loss issues.
- With the help of a monitoring tool, analyze the types of applications generating large data transfers.
- Monitor the data transfer load in parallel to packet loss recurrence and analyze it. You can do an initiated test for that issue in order to identify the maximum data transfer rate possible using the network. You probably will need an help of an experted IT.
In parallel with raising an immediate alert once a network problem occurs, you are able to see what happened, including internet packet loss. By adding side-by-side graphs related to network traffic, it is easy to correlate between large data transfer volume and packet loss.
Recommended action :
If possible, move high-volume traffic like remote storage and backups onto a secondary network, or reschedule these tasks to periods of low SQL or server demand.
Compress the data before transferring it and make sure critical applications are prioritized.
In addition, increase the network bandwidth and upgrade your internet connection if possible in order to optimize the transfer process.
For significant changes, it is recommended to consult network specialists.
4-The connection is lost. Priority: Medium
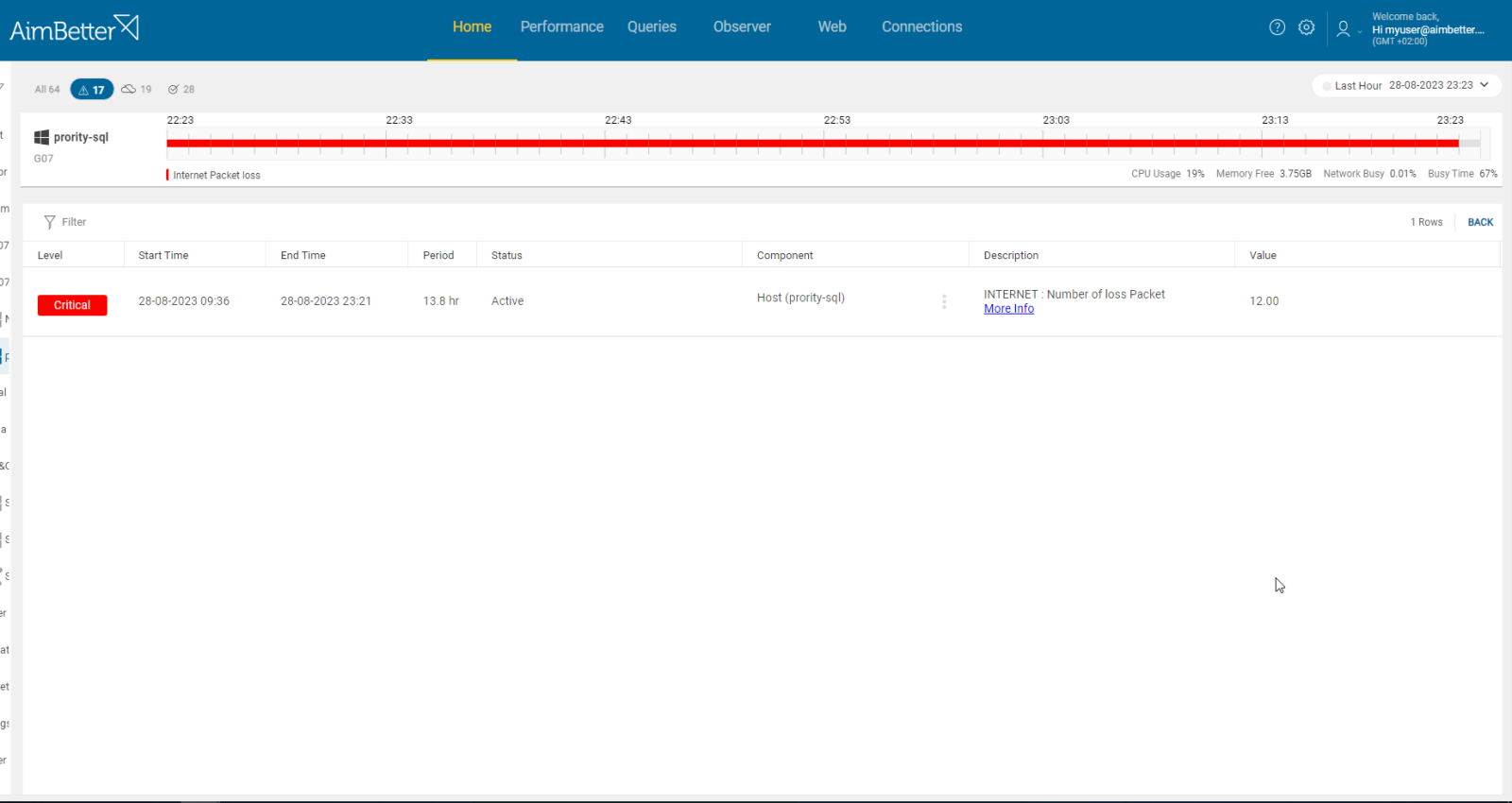
Loss of connection leads to immediate packet loss. In cases of complete disconnection, when 12 packets have been lost consecutively, several factors may be the cause, like router failure or errors, ISP failures, and component failures (router, bridge, other hardware on the agent’s server).
Problem identification:
Check the physical environment, internet availability, or router shutdowns.
- Try to access the internet with several different devices to ensure that it is not a specific device issue. Try accessing it by opening a web browser and visiting different websites.
- Many applications, especially web browsers and email clients, display error messages when the internet is unavailable for connection.
- Check if the router is active.
Following AimBetter’s immediate notification about the occurrence of internet packet loss, you can see if there are internet problems in multiple devices by checking several servers in a single panel.
Understand what happened next to the event, accessing the Observer panel that brings categorized logs with the relevant details for the selected time frame.
Recommended action :
If only a specific server is experiencing packet loss, check its physical environment, replace faulty components and restore network functionality.
If the problem relates to internet availability, contact your ISP’s customer support to get assistance and resolve the issue.